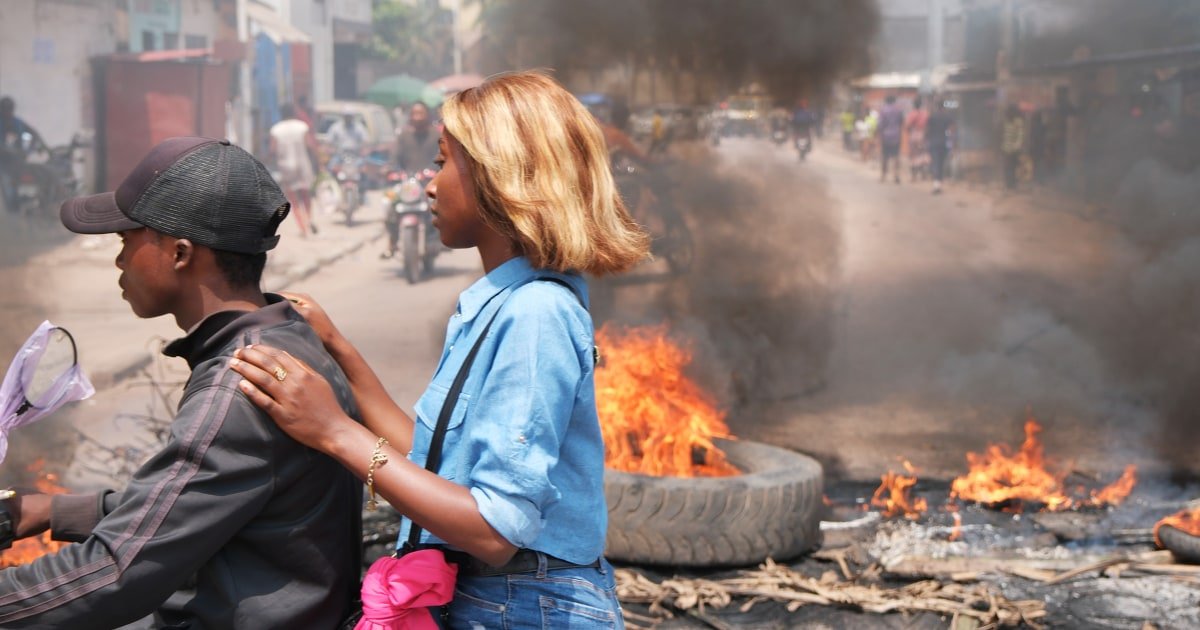
French Foreign Minister Jean-Noel Barot met with Tshisekedi in Kinshasa, after the French embassy, among others, was burned by protesters who protested against inaction by the international community.
President Donald Trump described this week the crisis as a “very serious problem”, while the State Department has advised US citizens who evacu China and Russia, for influence in the region.
“For the West, credibility is at stake,” said Nick Westcott, former director of the Royal African Society in Great Britain and currently a professor at the University of London Soas.
What is M23?
The M23 is a rebel group that has been involved in the ongoing ethnic conflict in the region since its beginning in 2012. The group is mainly composed of ethnic Tutsi who affirm that they fight for the rights of their minority group in the majority ethnic country- Ethnic Hutu Hutu.
The group was mainly formed as a result of the tension between the Rwanda Tutsi-Mayoria and the RDC. In 1994, Hutu’s militias in Rwanda committed what was later governed by the UN to be an ethnic genocide, with almost 1 million ethnic ethnic tutsi.
During and after the conflict, a group of ethnic Tutsi fled to the East RDC, near the borders with Rwanda and Burundi, which runs the risk of attracting war. Peace agreements, including a historic signed on March 23, 2009, have had mixed results. So, while some Tutsi rebels were integrated into the Congolese army, others splintered to form M23.
The UN has said in the past that M23 received military supplies and ammunition from the Rwanda Army. The president of Ruanda, Paul Kagame, a former rebel general Tutsi, has been accused of supporting M23. The group says that the Congolese government has not done enough to protect ethnic Tutsi in the country, and Rwanda denies providing weapons to militants.
What is China’s role?
Although the vast region is economically poor, in recent years it has become invaded by dozens of groups of armed militias, including one affiliated with the terrorist group of the Islamic State. These different groups have competed to benefit from the essential mineral trade for the global electronic supply chain that includes Coltan, Tantalum, Gold, Cobre and, perhaps more significantly, cobalt.