A private spacecraft is deprived of hours from trying to land on the moon, a feat that only another company has achieved in the history of space flight.
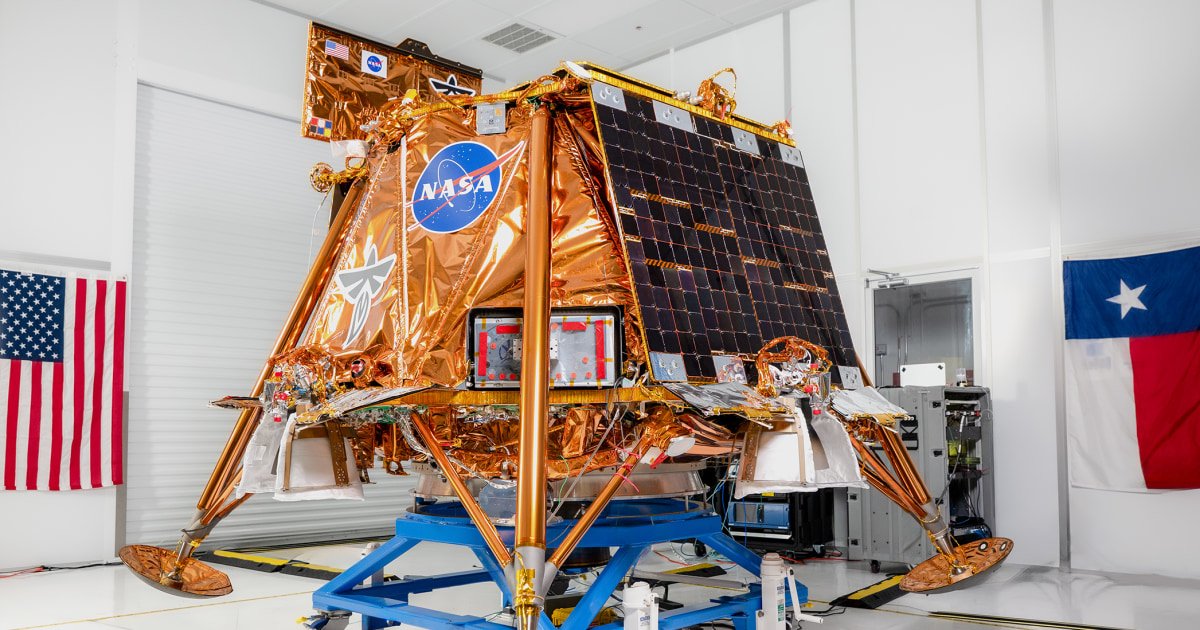
The robotic landing, called Blue Ghost, has been in orbit around the moon for approximately two weeks, preparing for its daring decline. The company based in Texas, Firefly Aerospace, developed the spacecraft, whose objective is to reduce the early lunar surface on Sunday at 3:34 am et.
If everything agrees with the plan, Blue Ghost will become the second private construction vehicle to land on the moon successfully. In February 2024, another company based in Texas, intuitive machines, made history when his Odysseus land achieved a touchdown to bite his nails near the South Pole of the Moon.
Firefly Aerospace’s next landing attempt is the first one in a burst of robotic missions to the moon in 2025. Earlier this week, intuitive machines launched their second scary to space, with a moon landing directed around March 6. Japanese company Ispace threw himself into the moon in the same rocket as Blue Ghost, but is taking a longer and less intensive path and is expected to arrive at the end of May or the beginning of June.
Blue Ghost aims to land in a 350 -wide width basin on the nearby side of the moon (the side that always faces the earth). It is believed that the region is the site of an ancient impact on asteroids, according to NASA.
Earlier this week, the shit landing transmitted the butt of the moon loaded with crater, loaded with crater, while orbiting approximately 62 miles on the surface.
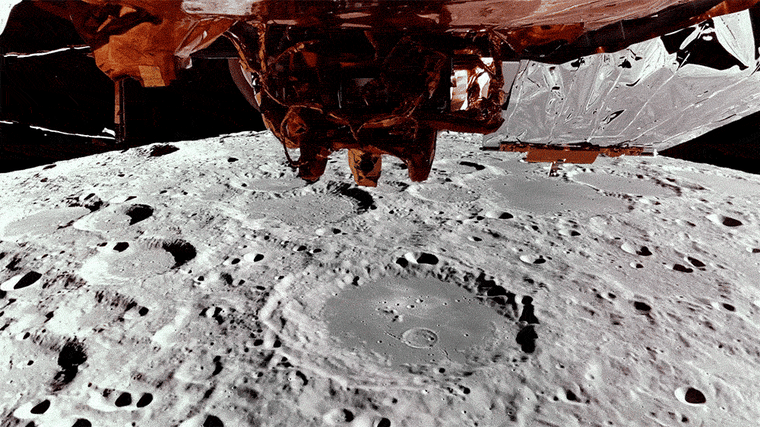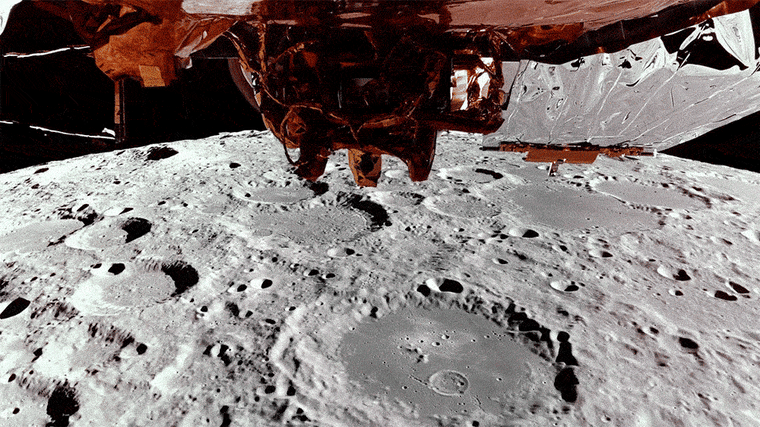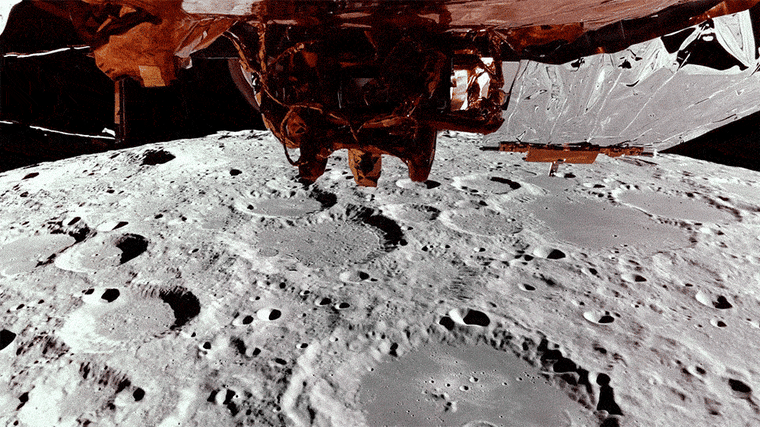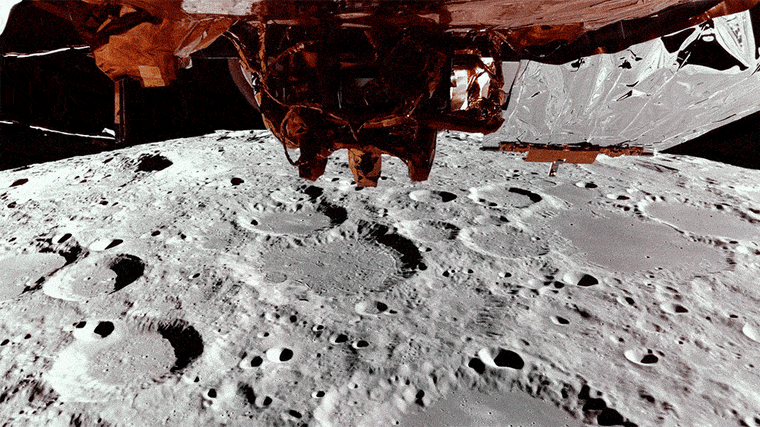
Blue Ghost is expected to begin his descent from one hour to the moon shortly after 2 in the morning on Sunday. NASA will broadcast a live broadcast from 2:20 am et on NASA television.
The spacecraft carries 10 scientific instruments of NASA, including one that will investigate the interior of the moon at depths of up to 700 miles. The cameras will take x -ray images looking back on the ground, studying how the space climate interacts with the earth’s magnetic field, while a separate camera will take detailed photos of the landing as it descends to the lunar surface to help future missions to the moon.
The instruments aboard the landing will also analyze samples of lunar soil, study how much moon dust adheres to different materials and use lasers to measure the precise distance between the earth and the moon.
Blue Ghost is expected to spend about two weeks collecting data on the lunar surface.
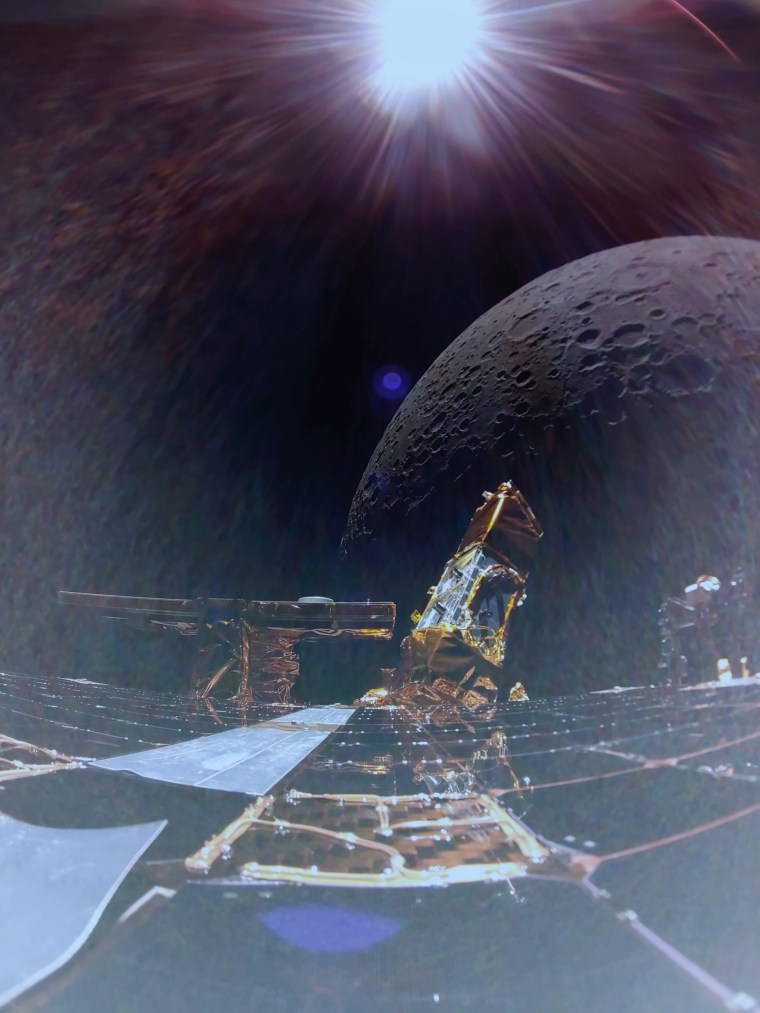

The mission is part of the NASA Commercial Lunar Load Services initiative, which was established as a public-private partnership between the agency and more than a dozen US companies to deliver NASA scientific experiments, technology and another load to the Moon. It is a component of the NASA Artemis program, whose goal is to eventually return humans to the moon.
The agency gave Firefly Aerospace around $ 101.5 million to carry out the Ghost Blue mission.
NASA has said that scientific experiments and technological demonstrations in these missions will help scientists better understand the Polar region of the southern moon, where future manned missions are expected to terror.









