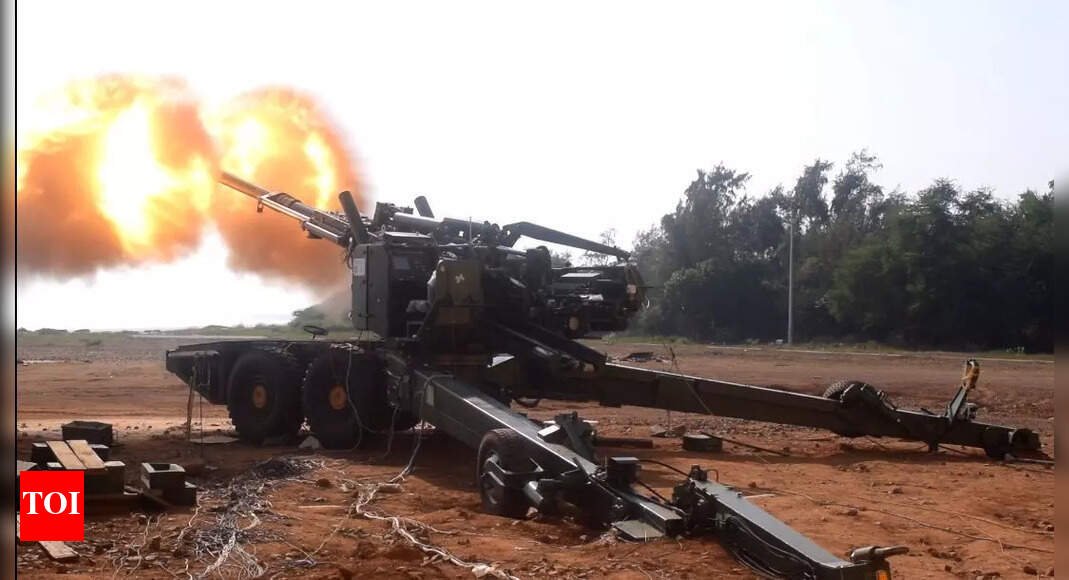
New Delhi: el Ministry of Defense On Wednesday he signed the contract of around 6,900 million rupees for the production of 307 advanced towing weapons weapons (Tags) and 327 vehicles of high mobility 6×6 that carry weapons with private sector companies Bharat Forge and Advanced Tata Systemsin the first agreement for such indigenous heavy -duty obuses.
With the signing of the agreement for the ATAG of 155 mm/52 calibers designed and developed by DRD, the total value of the capital acquisition contracts signed by MOD in the current prosecutor is of RS 1.4 Lakh million rupees. The Cabinet Security Committee led by PM had eliminated the ATAGs agreement on March 19, as Toi reported for the first time.
Defense Secretary Rajesh Kumar Singh congratulated the director of the ATAG project, which has a strike range of up to 45 km, depending on the ammunition, the establishment of research and development of armaments based in Pune de Drdo during the ceremony on Wednesday.
“The acquisition of this weapons system marks a significant milestone in the modernization of the Army Artillery Regiments, improving its operational preparation along the borders with China and Pakistan. Recognized for its exceptional lethality, the ATAGs will play a crucial role in reinforcing the army power when enabling the precise and long -term rays,” said an official.
Bharat Forge will manufacture 60% of the weapons because it had emerged as the L-1 (lowest bidder), while Tata will produce the remaining 40%. “The ATAG will replace the obsolete 105 mm and 130 mm cannons. More than 65% of its components are obtained nationwide, including key subsystems such as the barrel, the snout brake, the bedroom mechanism, the shooting and backward system, and the mechanism of management of ammunition,” said another official.
Officers say that ATAGs have an “excellent” precision, consistency, mobility, reliability and automation, longer maintenance operations due to their “electrical drive technology” and can fire bursts of five rounds compared to the bursts of three rounds by other contemporary foreign weapons.
The ATAG, whose development began in 2013, has undergone a prolonged field tests over the years. Finally, in 2021-22, winter tests were successfully completed in high altitude areas in Sikkim, which were followed by summer user start tests in Pokhran field shooting ranges.
The ongoing Russia-Ukraine War has again brought home the operating utility of long-range long-range fire power. Consequently, the army is progressively intensifying the induction of obuses, missiles, rocket systems and Merodea ammunition, as reported by Toi previously.
In December, for example, the Ministry of Defense signed a contract of RS 7,629 million rupees with L&T in collaboration with Hanwha’s defense of South Korea for the acquisition of another 100 K-9 Vajra-T self-propelled with tracked weapons systems, which have an attack range of 28-38 km and can be deployed in the areas of high altitude along the front of the front of the front.
Then, in February, modified MOD contracts worth 10,147 million rupees for extended high-explosive rockets (45 km range) and area denial ammunition (37 km) for indigenous pinaka multi-lanzer rock system that are indicated by the army. Pinaka is also exporting to other countries.
India has dealt with recurring scandals in the importation of Artillery gunsFrom the Swedish Bofors in the mid -1980s to the South African Denel in 2005 and the Singapore technology kinetics in 2009, repeatedly derailing the impulse of army modernization.